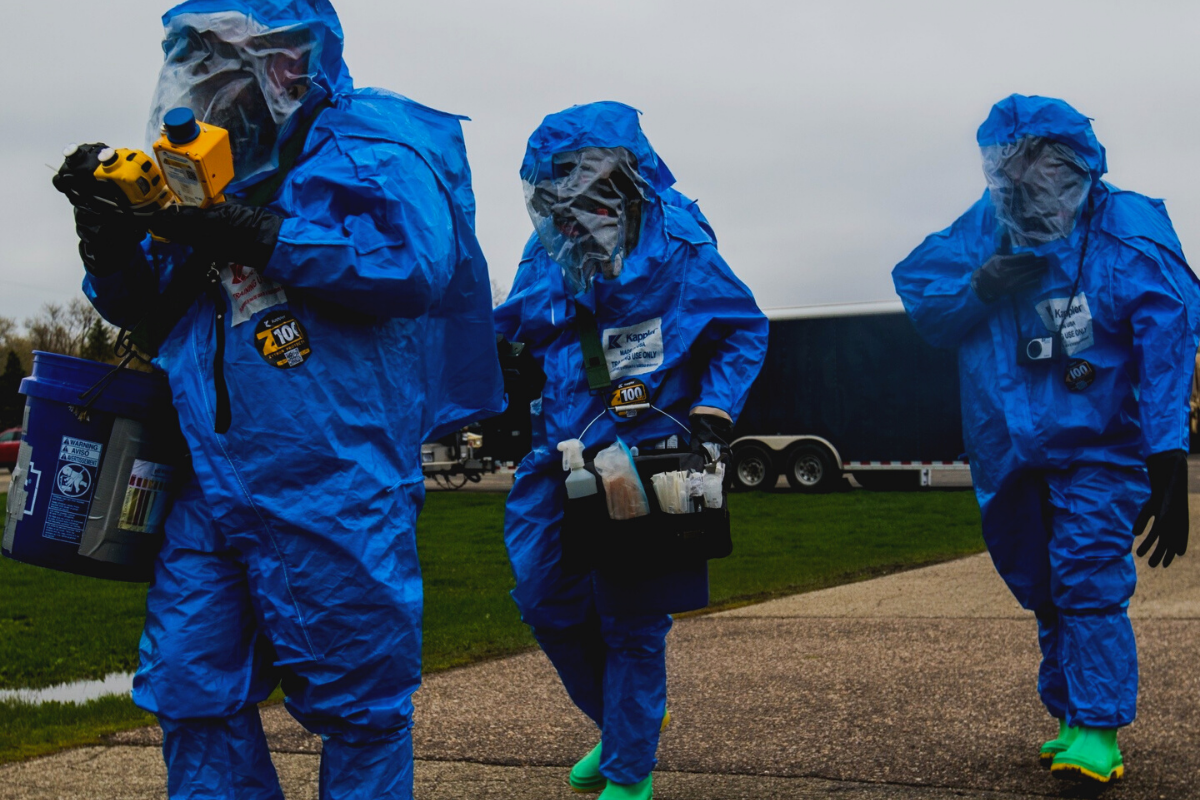
Hazardous materials (HAZMAT) are a broad category of substances that pose a potential threat to human health and the environment. They encompass a wide range of items, from everyday cleaning products to industrial chemicals, explosives, and radioactive materials. Given the inherent risks associated with HAZMAT, it’s crucial for safety professionals to have a deep understanding of their identification, safe handling, storage, and disposal procedures. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide, providing an overview of HAZMAT classification, regulations, and essential safety practices. We’ll also explore some interesting facts about hazardous materials and delve into the resources available through Advanced Safety & Training, including relevant courses like HAZCOM Training, Chemical Carcinogen Training, and HAZMAT Training.
Understanding Hazardous Materials
The first step toward ensuring safety with HAZMAT is understanding what constitutes hazardous materials. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a material is classified as hazardous if it exhibits a physical hazard or a health hazard. Physical hazards encompass materials that are flammable, explosive, unstable, corrosive, or reactive. Health hazards, on the other hand, can cause adverse health effects through inhalation, ingestion, skin absorption, or even simple eye contact. Examples of health hazards include toxic substances, carcinogens, and respiratory irritants.
There are numerous classification systems used to categorize HAZMAT based on their specific properties and potential hazards. A common system in the United States is the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS). The GHS uses a standardized approach with pictograms, signal words, and hazard statements to convey critical information about a hazardous material. This system ensures clear and consistent communication of risks across different languages and regions.
Regulatory Landscape for Hazardous Materials
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established a comprehensive regulatory framework for safeguarding workers from the hazards of hazardous materials. The Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom 2012) is a cornerstone of this framework. HazCom requires employers to maintain a Hazard Communication Program that includes creating and maintaining a written hazard communication plan, labeling containers of hazardous chemicals, providing safety data sheets (SDSs), and conducting employee training.
Beyond OSHA, various other federal and state agencies play a role in regulating HAZMAT, depending on the specific material and the context in which it’s used. For instance, the Department of Transportation (DOT) has regulations governing the safe transportation of hazardous materials. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the management and disposal of hazardous waste.
Safe Handling and Storage of Hazardous Materials
The safe handling and storage of hazardous materials are paramount to preventing accidents and protecting workers’ health. Safety professionals should be familiar with the specific hazards associated with the materials used in their workplaces. Consulting the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is crucial, as it provides detailed information on the physical and health hazards, safe work practices, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, and first-aid procedures. Here are some general best practices for safe handling and storage of HAZMAT:
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) based on the specific hazard.
- Maintain good ventilation in areas where hazardous materials are used.
- Store hazardous materials in designated and properly labeled containers.
- Segregate incompatible materials to prevent dangerous reactions.
- Train workers on safe handling procedures and emergency response protocols.
Interesting Facts About Hazardous Materials
The world of hazardous materials is filled with fascinating facts. Did you know that some seemingly innocuous items can be classified as HAZMAT? Common household products like nail polish remover, gasoline, and even some cleaning supplies can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here are a few more interesting tidbits:
The first known use of the term “hazardous material” can be traced back to the 18th century, referring to explosives used in warfare.
Radium, a naturally occurring radioactive element, was once used in everyday products like luminous watch dials and toothpaste due to its glowing properties. However, its harmful health effects were later discovered, leading to a ban on its use in consumer products. The development of the GHS classification system is a remarkable example of international cooperation in ensuring safe handling of chemicals across borders.
Advanced Safety & Training: Your Resource for HAZMAT Expertise
At Advanced Safety & Training, we understand the critical role safety professionals play in protecting workers from hazardous materials. We offer a comprehensive suite of courses designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of HAZMAT safety. Consider enrolling in the following courses to enhance your expertise:
- HAZCOM Training: This course provides a thorough understanding of the Hazard Communication Standard, including proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDSs), and understanding of Hazardous Communication practice in the workplace.
- Chemical Carcinogen Training: Delve deeper into the identification, safe handling, and the risks and protection surrounding carcinogenic chemicals in the workplace. This course will equip you to protect workers from the potential hazards of these hazardous materials.
- HAZMAT Training: This comprehensive course provides in-depth knowledge on hazardous materials classification, safe work practices, and personal protective equipment (PPE) selection.
By taking advantage of these courses, you can gain the confidence and competence to effectively manage HAZMAT in your workplace and ensure the safety and well-being of your workers. Hazardous materials are a prevalent reality in many workplaces. By understanding their classification, the relevant regulations, and safe handling practices, safety professionals can play a vital role in mitigating risks and protecting workers’ health. Advanced Safety & Training offers a valuable resource for those seeking to enhance their knowledge and expertise in HAZMAT safety. Remember, investing in safety is an investment in the well-being of your workforce and the success of your organization.




Recent Comments