Grounding and Bonding
Grounding and Bonding
Grounding and Bonding: When flammable and combustible liquids travel through a pipe or through the air, static charges are accumulated. Grounding and bonding is necessary during the transfer of flammable liquids that have a flashpoint below 100° F to prevent a static spark from igniting the flammable vapors.
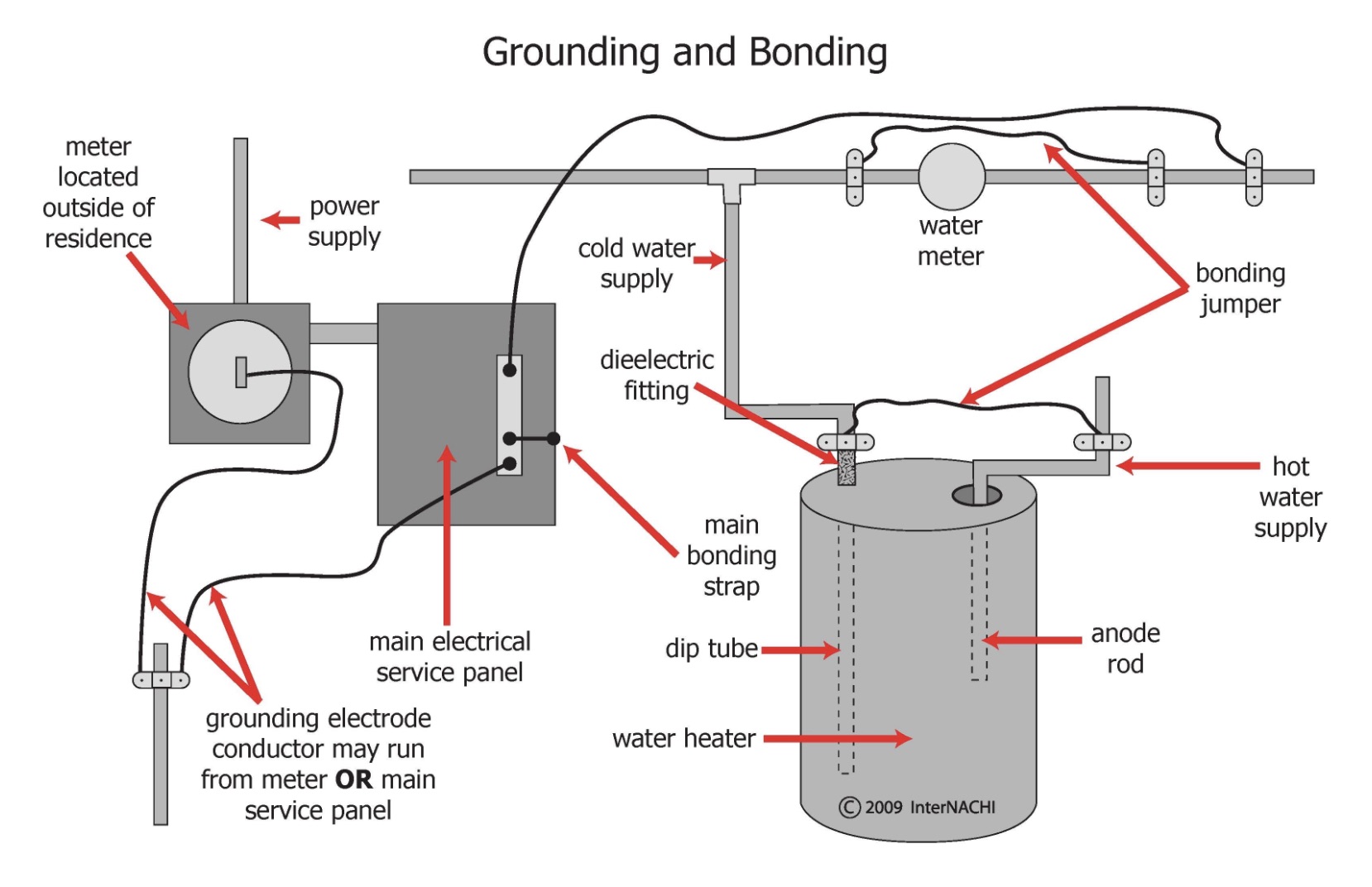
Both the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have bonding and grounding requirements. NFPA addresses the need for bonding and grounding in NFPA 30, the Flammable and Combustible Code. In the 2015 edition of NFPA 30, Chapter 18 Part 5.2.2 states that a means must be provided to minimize the generation of static electricity when transferring flammable liquids. NFPA 77, Recommended Practice on Static Electricity, covers the fundamental principles of effectively managing static electricity. This means all containers of Category 1, 2 or 3 liquids (liquids with a flashpoint lower than 100°F) need to be bonded and grounded during dispensing.
